Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Yokota, Yuichiro; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
We had developed the heavy-ion collimating microbeam system at TIARA of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), and utilized for analyzing heavy-ion induced biological effects. However, there is a difficulty in generating finer beam that is capable for carrying out precise subcellular irradiation in our current system, because of inevitable scattering of ions at the edge of micro collimator. Therefore, we installed new focusing microbeam system at another vertical beam line of AVF cyclotron of TIARA, JAEA. New system can focus heavy-ion beam to minimum 1  m in vacuum using a quadruplet quadrupole lens system, and equipped with an X, Y beam scanner for fast hitting of single ion to micron scaled samples. Using the system, irradiation of HeLa cells which was stained with Cell Tracker Orange fluorescent dye and inoculated on ion track detector CR39 film of 100
m in vacuum using a quadruplet quadrupole lens system, and equipped with an X, Y beam scanner for fast hitting of single ion to micron scaled samples. Using the system, irradiation of HeLa cells which was stained with Cell Tracker Orange fluorescent dye and inoculated on ion track detector CR39 film of 100  m thick, were carried out.
m thick, were carried out.
Yamashita, Shinichi; Funtowiez, D.*; Maeyama, Takuya*; Midorikawa, Masamichi*; Oka, Toshitaka; Baldacchino, G.*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kimura, Atsushi; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Katsumura, Yosuke; et al.
no journal, ,
Product yields of water radiolysis are inevitably important in understanding detailed mechanism of indirect action of ionizing radiations. We have conducted yield measurement of main products such as hydrated electron, hydroxyl radical ( OH) and hydrogen peroxide. We have also developed a sensitive method to determine
OH) and hydrogen peroxide. We have also developed a sensitive method to determine  OH yield with a fluorescent probe. In the method, aqueous solution of coumarin-3-carboxylic acid (CCA) is irradiated and
OH yield with a fluorescent probe. In the method, aqueous solution of coumarin-3-carboxylic acid (CCA) is irradiated and  OH is scavenged by CCA, resulting in production of fluorescent product 7OH-CCA. Applying this method,
OH is scavenged by CCA, resulting in production of fluorescent product 7OH-CCA. Applying this method,  OH yield near the Bragg peak has been measured in this study because the Bragg peak is overlapped cancer position in actual therapy. Beams of C 290 and 135 MeV/u and so on were taken for irradiation at the biological irradiation port at HIMAC facility of NIRS. It was found that
OH yield near the Bragg peak has been measured in this study because the Bragg peak is overlapped cancer position in actual therapy. Beams of C 290 and 135 MeV/u and so on were taken for irradiation at the biological irradiation port at HIMAC facility of NIRS. It was found that  OH yield show minimal value around the Bragg peak for every ion beam and it drastically jumps up several times at just downstream of the Bragg peak. It is already well known that contributions of fragmentation particles become non-negligible for high-energy heavy ions. Thus, further consideration including fragmentations is necessary to separate contributions of different fragmentation particles. Such consideration is being attempted by using simulations with HIBRAC and PHITS.
OH yield show minimal value around the Bragg peak for every ion beam and it drastically jumps up several times at just downstream of the Bragg peak. It is already well known that contributions of fragmentation particles become non-negligible for high-energy heavy ions. Thus, further consideration including fragmentations is necessary to separate contributions of different fragmentation particles. Such consideration is being attempted by using simulations with HIBRAC and PHITS.
Oka, Toshitaka; Yamashita, Shinichi; Midorikawa, Masamichi*; Saiki, Seiichi; Muroya, Yusa*; Lin, M.; Kamibayashi, Masato*; Anzai, Kazunori*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Katsumura, Yosuke
no journal, ,
The oxygen radicals play a crucial role in biological oxidative damage. It is important to clarify behavior of hydroxyl and superoxide radicals, detection and quantification of these radicals are required. In present work, the reactivities of CYPMPO toward a hydrated electron and a hydroxyl radical utilizing a pulse radiolysis system are investigated, and compared with DMPO (5,5-Dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide) results. The oxygen radicals produced by  -ray irradiation are also discussed.
-ray irradiation are also discussed.
Sato, Katsutoshi*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Okano, Yasuaki*; Hasegawa, Noboru; Ishino, Masahiko; Oshima, Shinsuke*; Numasaki, Hodaka*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Teshima, Teruki*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yokoya, Akinari; Ushigome, Takeshi*; Tauchi, Hiroshi*; Suzuki, Masao*; Tsuruoka, Chizuru*; Noguchi, Miho; Fujii, Kentaro; Shikazono, Naoya; Watanabe, Ritsuko
no journal, ,
In order to clarify the characteristics of DNA damage induced by high LET radiation, the yields of strand breaks and base lesions induced in closed-circular plasmid DNA (pUC18) were measured after exposing to various kinds of radiation (He, Ne and C ions; 2 to 900 keV/ m). Base excision repair enzymes were used to detect oxidative base lesions. The obtained results show that (1) the yield of prompt SSBs does not depend significantly on the LET, (2) whereas the yield of DSBs increases with increasing LET, (3) The yields of isolated nucleobase lesions detected by enzymes decrease drastically with increasing LET and (4) C and Ne ions induce less base lesions than He ions when compared in the same LET region. These results indicate that the yield of cluster of nucleobase lesions, which are less readily processed by the base excision repair proteins, depends not only LET but also ion species irradiated.
m). Base excision repair enzymes were used to detect oxidative base lesions. The obtained results show that (1) the yield of prompt SSBs does not depend significantly on the LET, (2) whereas the yield of DSBs increases with increasing LET, (3) The yields of isolated nucleobase lesions detected by enzymes decrease drastically with increasing LET and (4) C and Ne ions induce less base lesions than He ions when compared in the same LET region. These results indicate that the yield of cluster of nucleobase lesions, which are less readily processed by the base excision repair proteins, depends not only LET but also ion species irradiated.
Yokoya, Akinari
no journal, ,
We have measured the yield of DSB induced in hydrated pUC18 plasmid as a model DNA. TIARA in JAEA-Takasaki and HIMAC in NIRS were used as He, C and Ne ion beam sources. The track structures are different among the ions if they have the same LET values. Hence we have investigated the yield of DSB by systematically changing LET of identical ion. The obtained results show that (1) there is a minimum around 20 keV/ m for He ion irradiation, and the DSB yield increases precipitously toward 120 keV/
m for He ion irradiation, and the DSB yield increases precipitously toward 120 keV/ m, and then decreases again above the LET value, (2) similarly the yield of DSB increases with increasing level of LET of C ion in 80
m, and then decreases again above the LET value, (2) similarly the yield of DSB increases with increasing level of LET of C ion in 80 500 keV/
500 keV/ m though the trend is not noticeable rather than He ion irradiation, (3) the DSB yield does not significantly depend on LET for Ne ion irradiation. These results suggest that the DSB yield increases with increasing level of LET, though the trend of increase strongly depends on ion species.
m though the trend is not noticeable rather than He ion irradiation, (3) the DSB yield does not significantly depend on LET for Ne ion irradiation. These results suggest that the DSB yield increases with increasing level of LET, though the trend of increase strongly depends on ion species.
Hata, Kuniki; Katsumura, Yosuke; Lin, M.; Muroya, Yusa*; Fu, H.*; Yamashita, Shinichi; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Nakagawa, Keiichi*; Nakagawa, Hidehiko*
no journal, ,
Edaravone or RadiCut, 3-methyl-1-phenyl-2-pyrazolin-5-one, is a developed free radical scavenger that has been approved in Japan as a neuroprotective drug since 2001. For its antioxidative property and high reactivity with free radicals, edaravone has been expected as a radioprotector. In the last decade, the reactivity of edaravone with peroxyl radicals or some enzymes which induce oxidizing reactions, as well as the antioxidative properties of edaravone, have been extensively investigated. However, there are only a few reports on the measurements of the reactivity of edaravone towrads OH radical, although OH radical is thought to be a main factor of indirect radiation induced damages. In this work, we measured the reactivity of edaravone with OH radical, and elucidated its reaction mechanism. The reactions of edaravone and its model compound (1,3-dimethyl-2-pyrazolin-5-one) with OH radical or other oxidizing radicals were measured by pulse radiolysis techniques. The result shows that the intermediate radical produced by the reaction of edaravone with OH radical was spectroscopically different from that by the reactions with other radicals. On the other hand, for 1,3-dimethyl-2-pyrazolin-5-one, the intermediate radical by the reaction with OH radical is similar to that by the reaction with other oxidizing radical. All these strongly suggest that the phenyl group of edaravone plays an important role on the reaction with OH radical. Thus, in contrast to the previous reports in which the oxidation by OH radical was assumed to be through electron transfer or hydrogen abstraction from pyrazolin-5-one, the formation of OH adducts is crucial for the reaction of edaravone towards OH radical.
Fujii, Kentaro; Shikazono, Naoya; Yokoya, Akinari
no journal, ,
In order to verify the possibility of selective damage induction in DNA, the yields of base lesions as well as strand breaks have been measured in dry plasmid DNA films irradiated with highly monochromatized soft X-rays in the energy region of 270-760eV. The yields of base lesions were determined by the post-irradiation-treatment of the DNA with enzymatic probes (Fpg and Endo III) which excise base lesion. The yields of both pyrimidine and purine base lesions, observed as Nth-sensitive and Fpg-sensitive sites, respectively, are strikingly high at the oxygen K-edge (560eV) but extremely low at an energy just below the nitrogen K-edge (380eV) as compared with the yields observed at other photon energies. The yields at 560eV are enhanced 10-fold and 27-fold for Nth-sensitive and Fpg-sensitive sites, respectively, compared with those at 380eV. The yield of prompt single strand breaks is also enhanced at the oxygen K-ionization energy, but only 2-fold, as compared with that at 380eV.
Yoshihara, Ryohei; Hase, Yoshihiro; Nozawa, Shigeki; Takimoto, Koichi*; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
We irradiated carbon ion-beams (220-MeV C) and  -rays to
-rays to  carrying
carrying 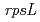 gene to analyze mutational effects of these radiations. Our results suggested that
gene to analyze mutational effects of these radiations. Our results suggested that  -rays might induce smaller size of deletion mutation compared to 220-MeV C. The induction of oxidized guanine by these radiations was low in dry seeds because of low incidence of G:C to T:A and A:T to C:G transversion in irradiated group.
-rays might induce smaller size of deletion mutation compared to 220-MeV C. The induction of oxidized guanine by these radiations was low in dry seeds because of low incidence of G:C to T:A and A:T to C:G transversion in irradiated group.  -ray-induced mutation analysis in
-ray-induced mutation analysis in  seedling was similar to that in dry seed, suggesting the mutational effect of radiation used here in higher plant might be different from that in other organisms.
seedling was similar to that in dry seed, suggesting the mutational effect of radiation used here in higher plant might be different from that in other organisms.
Watanabe, Ritsuko; Hirayama, Ryoichi*; Yokoya, Akinari; Terato, Hiroaki*; Tsuruoka, Chizuru*; Eguchi, Kiyomi*; Furusawa, Yoshiya*; Kobayashi, Katsumi*
no journal, ,
DNA double strand breaks (DSB) is thought to be the most critical damage for cell death. However, a considerable discrepancy is often observed between LET dependence of the frequency of cell death and that of the DSB yield. Also, several studies on the DSB yields as a function of LET have reported different tendency in the DSB-LET relationships. To obtain insight of the relationship between DSB and cell death, it is necessary to clarify the actual LET dependence of DSB. We have been discussing about the reason why the difference of the results depending on the groups. Here we will report on the results of our discussion. In particular, some points on the experimental detection system of DSB and the problems in calculation of absorbed dose (Gy) for particle beams will be discussed.

Shikazono, Naoya; Noguchi, Miho; Urushibara, Ayumi; O'Neill, P.*; Yokoya, Akinari
no journal, ,
Using a bacterial plasmid-based assay, we have investigated the biological consequences of bistranded clustered damage sites which are comprised of combinations of base lesions, AP sites, and SSBs. Plamids were ligated with oligonucleotides with clustered lesions. Following transformation of the ligated plasmids into wild type strain of Escherichia coli, clustered damage-induced mutations were characterized. Although the transformation efficiencies were low, the major types of mutation induced by the AP + AP or AP + SSB cluster were G insertion opposite AP and a 1-bp deletion at the base pair with AP. On the other hand, mutations were occasionally found at base pairs where lesions had not been placed with clusters such as DHT + 8-oxoG, and DHT + SSB. From these results, we suggest that, in a bistranded base cluster, (1) either base lesion is remained unrepaired and (2) some mutations arise not at but very close to the base pair where base lesions were originally placed.
Noguchi, Miho; Urushibara, Ayumi; Yokoya, Akinari; Shikazono, Naoya
no journal, ,
Clustered DNA damage is defined as two or more lesions generated within 1-2 helical turns (10-20bp) of DNA. Ionizing radiation has a characteristic to deposit energy to local area on DNA and to induce clustered DNA damage. Theoretical studies and experimental data suggest an increased complexity and severity of clustered DNA damage with increasing LET of ionizing radiation. It is proposed that ionizing radiation produces clustered DNA damage including single strand break (SSB) and double strand break (DSB) with several oxidative base lesions. It is postulated that clustered DNA damage is incompletely or incorrectly repaired, and is strongly related to biological effects, such as cell death and mutation. We measured mutation frequencies induced by two types of clustered damage carrying a SSB and an 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine (8-oxoG) each on the complementary strands or both on the same DNA strand in E. coli. We found that the clustered damage with 8-oxoG and SSB each placed on complementary strands had a higher mutation frequency than single 8-oxoG, while the clustered damage with 8-oxoG and SSB positioned on the same strand had a slightly lower mutation frequency than single 8-oxoG either in wild type or in glycosylase (Fpg and/or MutY) deficient mutants. These results suggest that SSB opposed to 8-oxoG retards the excision of 8-oxoG by formamidopyrimidine DNA glycosylase (Fpg). However, processing of the tandem lesion of SSB and 8-oxoG remains to be elucidated. In this study, using in vitro enzyme assay, we investigated the processing of clustered damage containing 8-oxoG and SSB on the same DNA strand.
Akamatsu, Ken
no journal, ,
Spectra of DNA damage induced by ionizing radiation are considered to be different among radiation qualities. Although investigators are obtaining information about the difference, it is difficult to conclude overall nature of DNA damage by means of only a method for detecting a DNA damage. So, it is expected that we can have new knowledge by comparing data obtained by two or more individual methodologies. So far, we have obtained some DNA damage information of 60Co  -rays, etc., by comparing data from analytical methods. For example, in yields for single strand break on dry DNA sample induced by 60Co
-rays, etc., by comparing data from analytical methods. For example, in yields for single strand break on dry DNA sample induced by 60Co  -rays, we found that the yield obtained by using phosphodiesterase I, by which calculating an absolute strand break yield, is 1.3 - fold larger than that obtained by super coiled plasmid method. This result implies that it is necessary for us to conclude nature of the damage under sufficient discussion about nature of a methodology.
-rays, we found that the yield obtained by using phosphodiesterase I, by which calculating an absolute strand break yield, is 1.3 - fold larger than that obtained by super coiled plasmid method. This result implies that it is necessary for us to conclude nature of the damage under sufficient discussion about nature of a methodology.
Yokota, Yuichiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Michiyo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
Here, we investigate a combination effect of carbon-ion irradiation and the telomerase inhibitor MST-312 treatment. Human cervical cancer HeLa cells were cultured for 24 h with or without 1  M MST-312, and then, irradiated with carbon ions (LET=110 keV/
M MST-312, and then, irradiated with carbon ions (LET=110 keV/ m) and
m) and  -rays. After irradiation, cells were reseeded in fresh medium without MST-312 and colonies were counted as described above. The survival of the irradiated cells additively decreased in combination with MST-312 treatment. Irradiation and MST-312 treatment might inactivate the clonogenic potential of tumor cells through independent mechanisms. The doses needed to reduce the survival of irradiated cells to 10% were decreased by MST-312 treatment from 1.2 Gy to 0.5 Gy (carbon-ion irradiation) and from 5.4 Gy to 4.0 Gy (
-rays. After irradiation, cells were reseeded in fresh medium without MST-312 and colonies were counted as described above. The survival of the irradiated cells additively decreased in combination with MST-312 treatment. Irradiation and MST-312 treatment might inactivate the clonogenic potential of tumor cells through independent mechanisms. The doses needed to reduce the survival of irradiated cells to 10% were decreased by MST-312 treatment from 1.2 Gy to 0.5 Gy (carbon-ion irradiation) and from 5.4 Gy to 4.0 Gy ( -ray irradiation), respectively. MST-312 pre-treatment may reduce the dose needed for a curative effect in heavy-particle radiotherapy.
-ray irradiation), respectively. MST-312 pre-treatment may reduce the dose needed for a curative effect in heavy-particle radiotherapy.

Suzuki, Michiyo; Hattori, Yuya; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Tsuji, Toshio*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
We examined the effects of ionizing radiation (IR) on locomotory behavior using  , and reported an IR-induced reduction of locomotory rate in the absence of food. In the previous experiments, wild-type animals were irradiated with
, and reported an IR-induced reduction of locomotory rate in the absence of food. In the previous experiments, wild-type animals were irradiated with  -rays in the whole body, and measured the motility using "body bends" (the number of bends in the anterior body region at 20-s intervals). However, the IR-induced effects in the central and posterior body region were not evaluated by the body bends. Therefore, we propose a novel method evaluating the motility of whole body by using the video-based analysis. Animals were irradiated with graded doses of
-rays in the whole body, and measured the motility using "body bends" (the number of bends in the anterior body region at 20-s intervals). However, the IR-induced effects in the central and posterior body region were not evaluated by the body bends. Therefore, we propose a novel method evaluating the motility of whole body by using the video-based analysis. Animals were irradiated with graded doses of  Co
Co  -rays. Immediately after irradiation, we video-recorded the animals, and analyzed the trajectories and bends at 17 points of the body. The proposed method provides some novel insight about the IR-induced changes on
-rays. Immediately after irradiation, we video-recorded the animals, and analyzed the trajectories and bends at 17 points of the body. The proposed method provides some novel insight about the IR-induced changes on  's locomotion.
's locomotion.